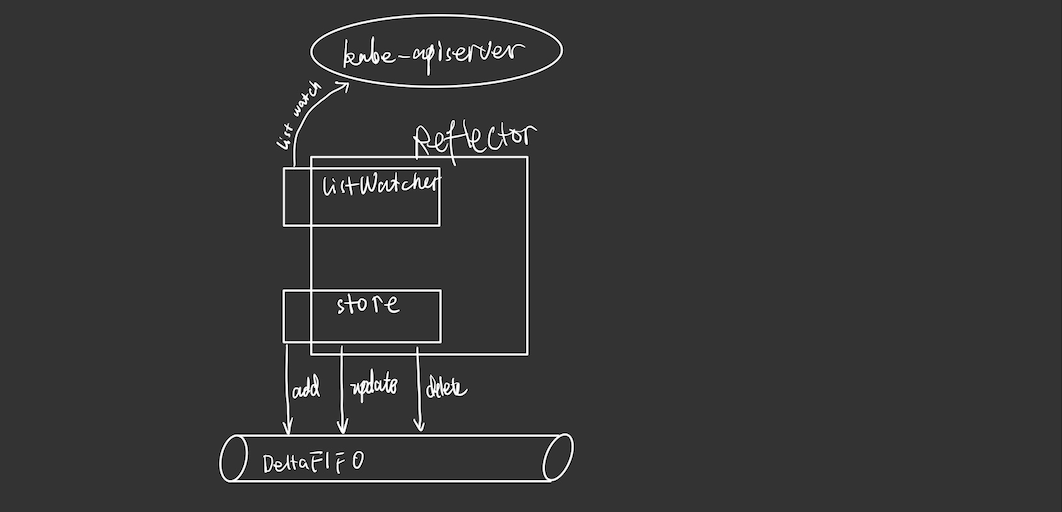
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
|
// ListAndWatch first lists all items and get the resource version at the moment of call,
// and then use the resource version to watch.
// It returns error if ListAndWatch didn't even try to initialize watch.
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
var resourceVersion string
options := metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()}
// list部分
if err := func() error {
var list runtime.Object
var paginatedResult bool
var err error
listCh := make(chan struct{}, 1)
panicCh := make(chan interface{}, 1)
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
panicCh <- r
}
}()
// Attempt to gather list in chunks, if supported by listerWatcher, if not, the first
// list request will return the full response.
pager := pager.New(pager.SimplePageFunc(func(opts metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.listerWatcher.List(opts)
}))
switch {
case r.WatchListPageSize != 0:
pager.PageSize = r.WatchListPageSize
case r.paginatedResult:
// We got a paginated result initially. Assume this resource and server honor
// paging requests (i.e. watch cache is probably disabled) and leave the default
// pager size set.
case options.ResourceVersion != "" && options.ResourceVersion != "0":
pager.PageSize = 0
}
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), options)
if isExpiredError(err) || isTooLargeResourceVersionError(err) {
r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(true)
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()})
}
close(listCh)
}()
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
case r := <-panicCh:
panic(r)
case <-listCh:
}
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to list %v: %v", r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
// We check if the list was paginated and if so set the paginatedResult based on that.
// However, we want to do that only for the initial list (which is the only case
// when we set ResourceVersion="0"). The reasoning behind it is that later, in some
// situations we may force listing directly from etcd (by setting ResourceVersion="")
// which will return paginated result, even if watch cache is enabled. However, in
// that case, we still want to prefer sending requests to watch cache if possible.
//
// Paginated result returned for request with ResourceVersion="0" mean that watch
// cache is disabled and there are a lot of objects of a given type. In such case,
// there is no need to prefer listing from watch cache.
if options.ResourceVersion == "0" && paginatedResult {
r.paginatedResult = true
}
r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(false) // list was successful
initTrace.Step("Objects listed")
listMetaInterface, err := meta.ListAccessor(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v: %v", list, err)
}
resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()
initTrace.Step("Resource version extracted")
items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v (%v)", list, err)
}
initTrace.Step("Objects extracted")
if err := r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to sync list result: %v", err)
}
initTrace.Step("SyncWith done")
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
initTrace.Step("Resource version updated")
return nil
}(); err != nil {
return err
}
// resync部分
resyncerrc := make(chan error, 1)
cancelCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(cancelCh)
go func() {
resyncCh, cleanup := r.resyncChan()
defer func() {
cleanup() // Call the last one written into cleanup
}()
for {
select {
case <-resyncCh:
case <-stopCh:
return
case <-cancelCh:
return
}
if r.ShouldResync == nil || r.ShouldResync() {
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: forcing resync", r.name)
if err := r.store.Resync(); err != nil {
resyncerrc <- err
return
}
}
cleanup()
resyncCh, cleanup = r.resyncChan()
}
}()
// watch部分
for {
// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errors
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
default:
}
timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))
options = metav1.ListOptions{
ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any wachers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
}
// start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sent
start := r.clock.Now()
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
// If this is "connection refused" error, it means that most likely apiserver is not responsive.
// It doesn't make sense to re-list all objects because most likely we will be able to restart
// watch where we ended.
// If that's the case begin exponentially backing off and resend watch request.
if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) {
<-r.initConnBackoffManager.Backoff().C()
continue
}
return err
}
if err := r.watchHandler(start, w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh); err != nil {
if err != errorStopRequested {
switch {
case isExpiredError(err):
// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already
// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.
// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
default:
klog.Warningf("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
}
return nil
}
}
}
|